Breakthrough in CO2 Reduction
Our Recent Publication on Zero-Gap Gas Phase Photoelectrolyzer with Porous Carbon Supported Photocathodes
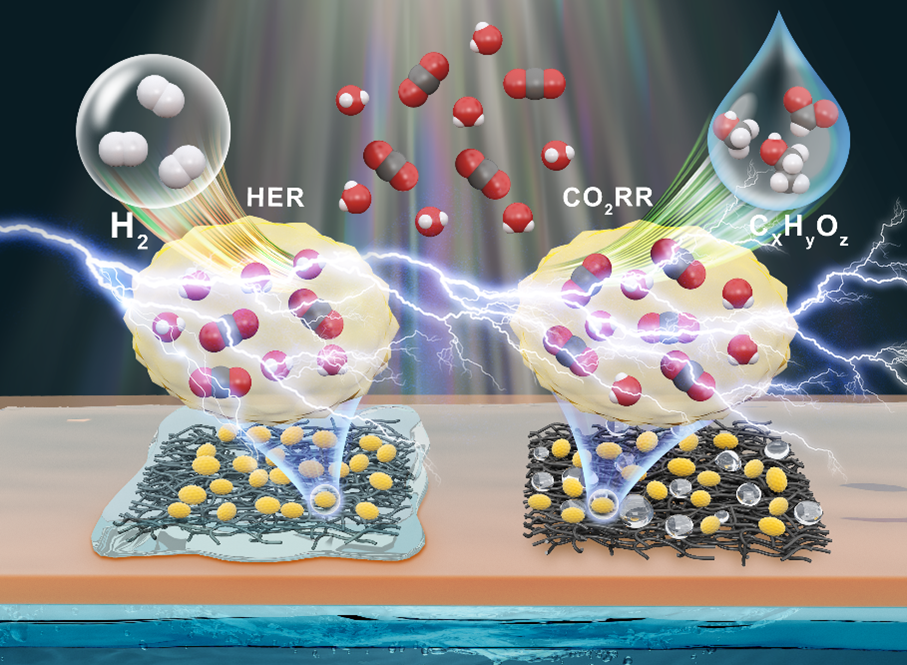
With their variable active sites metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) can achieve visible-light absorption and efficient charge separation for photocatalytic, and conductivity for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction into value added chemicals. This work illustrates the importance of porous carbon fiber layers (CFLs) on the activity and selectivity of MOF based photocathodes towards the CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) in a zero-gap gas phase photoelectrolyzer. The wettability of the CFL modulates the local environment on the metal organic framework catalyst (UiO-66-NH2, yellow coloured). Hydrophobic CFL-based MOF photocathodes lead to CO2RR, producing liquid hydrocarbons (CxHyOz) such as formate, methanol and ethanol. In contrast, hydrophilic, wetted CFL-based photocathodes favor the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER). The results are a step further in understanding how the design and composition of the photoelectrodes in photoelectrochemical electrolyzers can impact the CO2 reduction efficiency and selectivity.